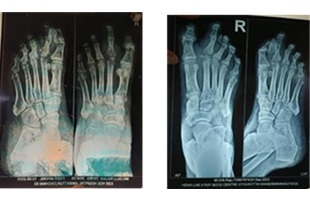
An Approach to Wound Healing in Dusta Vrana (Diabetic Foot Ulcer) with Ayurveda Formulations: A Case Report

DOI:
https://doi.org/10.54060/a2zjournals.ijahr.49Keywords:
Diabetic foot ulcer, Dusta vrana, Guggulutiktakam Kashayam, Diabetic angiopathyAbstract
Background: Diabetic Foot Ulcer (Dustavrana) is a common complication of Diabetes Mellitus. Sometimes Diabetic foot ulcer left unnoticed or improper management usually paves way to develop an infection affecting the foot, along with osteomye-litis which can even lead to amputation of the lower limb. This creates practical difficulty Physically and psychologically to the patient and for their kith and kins. So, proper treatment should be adopted as a measure for saving the lower limb from further infections as a preventive measure and complete healing should be aimed at without much difficulty. Materials and Methods: This article mentions a case report of the Diabetic foot ulcer managed through Ayurveda medications internally and proper wound care externally. Result: Ayurvedic medicines were able to manage the diabetic foot ulcer very effectively.
Downloads
References
McMillan DE. Diabetic angiopathy--its lessons in vascular physiology. Am Heart J. 1978 Sep;96(3):401-6. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(78)90053-4. PMID: 356570.
Deshpande AD, Harris-Hayes M, Schootman M. Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetes-related complications. Phys Ther. 2008 Nov;88(11):1254-64. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20080020. Epub 2008 Sep 18. PMID: 18801858; PMCID: PMC3870323.
Deshpande AD, Harris-Hayes M, Schootman M. Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetes-related complications. Phys Ther. 2008 Nov;88(11):1254-64. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20080020. Epub 2008 Sep 18. PMID: 18801858; PMCID: PMC3870323.
Ghosh P, Dey A, Gupta A. Burden of diabetic foot ulcers in India: evidence landscape from published literature. Value Health. 2017;20(9):A485.
Sahu SS, Chaudhary V, Sharma N, Singh H. Prevalence and risk factors associated with diabetic foot ulcer in India: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s13410-024-01400-x.
Kunte AM. Astangahrdaya of Vagabhatta. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Sansthan; 2011 (Reprint). Chapter 21, Vatvyadhi Chikitsa Sthanam, p. 726.
Kim KH, Jung JH, Chung WS, Lee CH, Jang HJ. Ferulic acid induces keratin 6α via inhibition of nuclear β-catenin accu-mulation and activation of Nrf2 in wound-induced inflammation. Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 22;9(5):459. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050459. PMID: 33922346; PMCID: PMC8146113.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
CITATION COUNT
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr Aparna Mambally, Dr Ravendra Kumar Tiwari, Dr T Udaya Kiran, Dr K Vasudeva Reddy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.























